Accidents can happen in an instant. One moment, you're slicing vegetables— the next, there's blood. Do you know what to do?
Stopping bleeding quickly can mean the difference between a minor wound and a serious emergency. A small cut might seem harmless, but without proper care, it can lead to infection or excessive blood loss.
What if it’s a deep wound? What if the bleeding won’t stop?
Don’t panic. This guide will show you simple, life-saving first-aid techniques. Step by step, you’ll learn how to control bleeding, protect the wound, and know when to call for help. Because in an emergency, every second counts.
👉 Be prepared! Check out our guide on Emergency First Aid Kits: Must-Have Safety Gear to ensure you're ready for any situation.
Assessing the Severity of the Bleeding
Before you begin treatment, it's crucial to determine whether the bleeding at home is minor or severe.
Minor Bleeding:
- Slow, oozing blood from small cuts or scrapes.
- Stops within a few minutes with direct pressure.
Severe Bleeding:
- Continuous or spurting blood.
- Deep wounds exposing muscle or bone.
- Blood soaking through multiple bandages quickly.
🚨 Seek Medical Help If:
- Bleeding does not stop after 10-15 minutes of direct pressure.
- The wound is deep, jagged, or caused by a dirty object.
- The injured person feels weak, dizzy, or pale.
Step-by-Step First Aid for Bleeding Control
If the bleeding at home is manageable, follow these first-aid for bleeding steps:
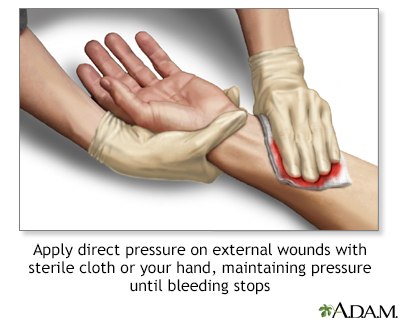
1. Apply Direct Pressure
The most effective way to stop bleeding is to press firmly on the wound with a clean cloth or bandage. Maintain steady pressure without lifting to check if the bleeding has stopped.
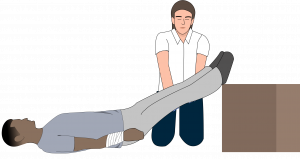
2. Elevate the Injured Area
Raise the injured limb above heart level to reduce blood flow to the wound. This helps slow down bleeding by using gravity to decrease pressure in the affected area.
Elevation, combined with direct pressure, can significantly improve bleeding control and prevent excessive blood loss. Keep the limb supported and still to maximize effectiveness.
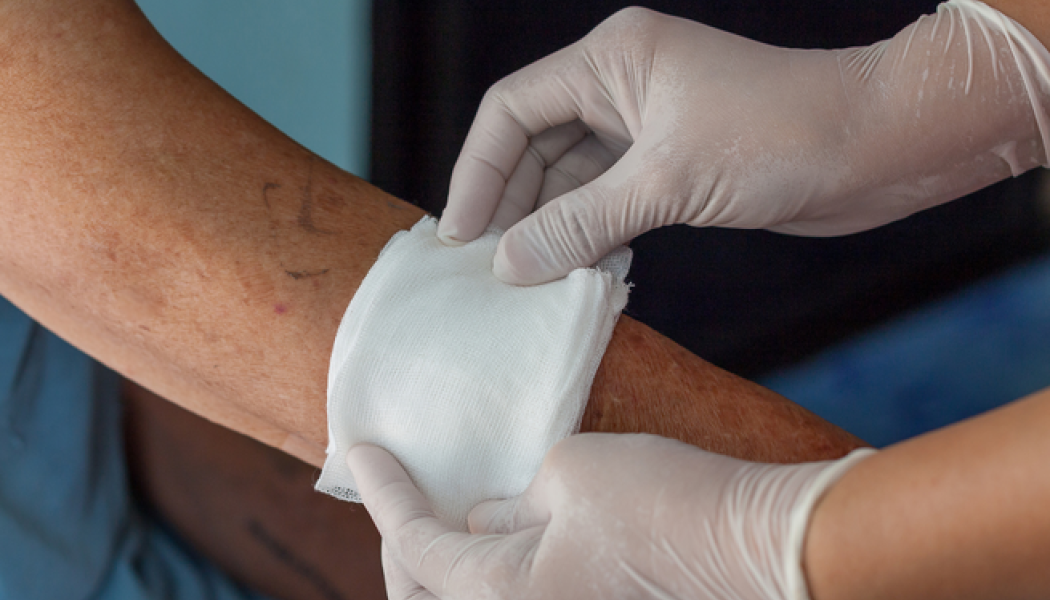
3. Use a Clean Bandage for Bleeding Control
- If blood soaks through, do not remove the initial layer—add another layer on top.
- Secure the dressing with medical tape or a clean bandage.
👉 Learn more about the importance of bandages in first aid: Bandages: The Unsung Heroes of First Aid Kits You Can't Ignore.
4. Consider Hemostatic Agents
If available, apply a hemostatic dressing or powder to help with immediate bleeding cessation, especially for severe wounds.
Special Cases: First Aid for Different Types of Bleeding
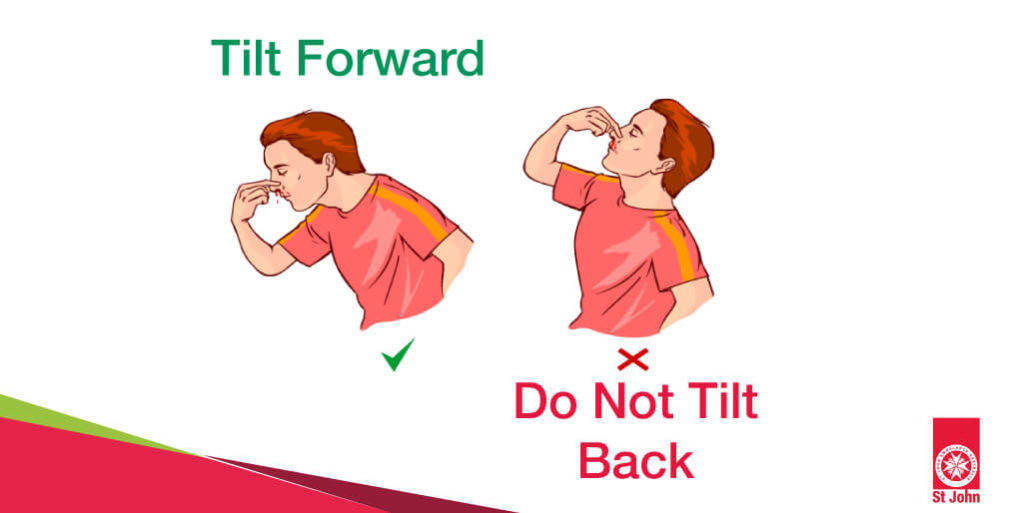
Nosebleeds
- Sit upright and lean slightly forward.
- Pinch the nostrils together for 5-10 minutes.
- Avoid tilting the head back to prevent swallowing blood.
Deep Cuts and Puncture Wounds
- Do not remove any embedded objects.
- Apply firm pressure around the object.
- Seek emergency wound management immediately.
Bleeding from the Head or Face
- Apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth.
- If a head injury is suspected, seek first-response care.
Preventing Infection After Stopping Bleeding
Once you achieve wound stabilization, it’s essential to clean and protect the wound to prevent infection.
How to Clean the Wound:
- Rinse with clean water or saline solution.
- Apply an antiseptic ointment.
- Cover with a sterile bandage for bleeding control.
Signs of Infection to Watch For:
- Redness, swelling, or warmth around the wound.
- Pus or unusual drainage.
- Fever or increased pain.
When to Seek Emergency Bleeding Assistance
Go to the hospital if:
- Bleeding persists despite applying direct pressure and a bandage.
- The wound is deep and exposes muscle or bone.
- The injury is from a dirty or rusty object (risk of tetanus).
- The person shows signs of shock (pale skin, dizziness, rapid breathing).
Basic First Aid Remedies for Bleeding at Home
If you don’t have a first aid kit on hand, you can use everyday items for DIY first aid treatment:
- Clean Cloth or Towel: For applying pressure to wounds.
- Plastic Wrap or Clean Bag: To create a makeshift barrier.
- Honey or Aloe Vera: Natural remedies that can help with healing.
- Cold Compress: Helps reduce swelling and pain.
Conclusion
Knowing how to stop bleeding at home using self-administered first aid is a life-saving skill. By using direct pressure, elevating the injured area, and ensuring proper wound care, you can prevent complications.
Always have a home first aid kit stocked with essentials for injury management at home. If bleeding does not stop, seek medical help immediately.
👉 Stay prepared—having emergency wound management knowledge can make all the difference!